String
1 String
- 자바의 문��자열은 java.lang 패키지의 String 클래스의 인스턴스로 관리된다.
- 소스상에 문자열 리터럴은 String 클래스로 자동 생성되지만 String 클래스의 다양한 생성자를 이용해서 직접 String 클래스를 생성할 수도 있다.
- 코드에서 문자열 리터럴이 발견될 때마다 컴파일러는 문자열 객체를 만든다.
String Literal
- 소스 코드에 작성된 문자열
- 큰 따옴표로 묶는다.
- 아래에
Hello world!가 문자열 리터럴이다.
String greeting = "Hello world!";
2 Immutable
- immutable이란?
- 객체의 내부 상태가 생성 후 변하지 않는 것을 의미한다.
- String 클래스에는 여러 가지 메서드가 있으며, 그 중 일부는 문자열을 수정하는 것처럼 보인다.
- 하지만 문자열은 변경되지 않으므로(immutable) 메서드는 작업을 수행한 새 문자열을 만들고 반환한다.
- String의 replace() 메소드는 첫 번째 매개값인 문자열을 찾아 두 번째 매개값으로 대치한 완전히 새로운 문자열 생성하고 반환한다.
- immutable의 장점
- 캐싱
- 보안
- 동기화
- 성능
3 String Pool
- String이 저장되는 메모리의 특수한 공간을 의미한다.
- String은 immutable하기 때문에 JVM은 String에게 할당되는 메모리의 양을 최적화할 수 있다.
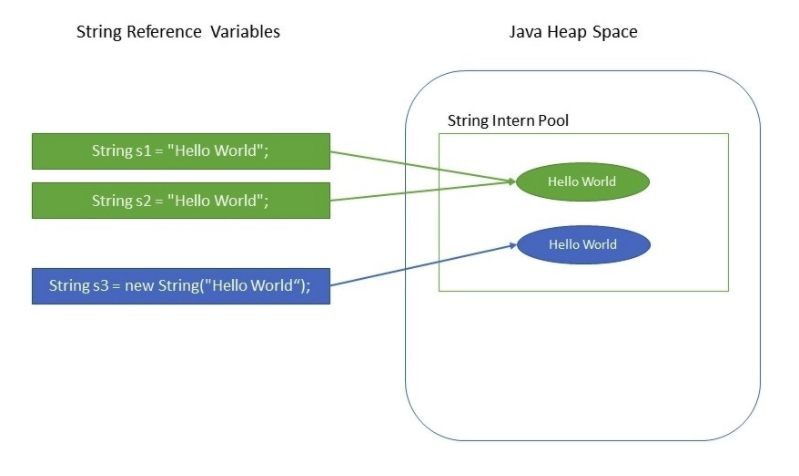
- 오직 하나의 String객체를 String Pool에 생성하고 여러개의 다른 변수들이 하나의 같은 String 객체를 가르키게하여 메모리 자원을 절약할 수 있다.
// s1과 s2 모두 String Pool의 같은 String 객체를 가르키기 때문에 결과는 True이다.
String s1 = "Hello World";
String s2 = "Hello World";
assertThat(s1 == s2).isTrue();
- 메모리 구조
- s1과 s2 모두 String Pool의 같은 String 객체를 가르키고 있다.
String 비교 예시
public class StringEqualsExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String strVar1 = "노영삼";
String strVar2 = "노영삼";
if (strVar1 == strVar2) {
System.out.println("strVar1과 strVar2는 참조가 같음.");
} else {
System.out.println("strVar1과 strVar2는 참조가 다름.");
}
String strVar3 = new String("노영삼");
String strVar4 = new String("노영삼");
if (strVar3 == strVar4) {
System.out.println("strVar3과 strVar4는 참조가 같음.");
} else {
System.out.println("strVar3과 strVar4는 참조가 다름.");
}
if (strVar3.equals(strVar4)) {
System.out.println("strVar3과 strVar4는 문자열이 같음.");
}
}
}
//결과
strVar1과 strVar2는 참조가 같음.
strVar3과 strVar4는 참조가 다름.
strVar3과 strVar4는 문자열이 같음.
4 immutable의 장점
4.1 Caching
- String의 hash 값은 빈번히 사용된다.
- HashMap, HashTable, HashSet 등에서
- String의 hashCode() 메서드는 빈번히 호출된다는 의미다.
- String은 immutable하기 때문에 값이 변하지 않는다.
- 따라서 hashCode()를 캐싱을 사용하도록 구현할 수 있다.
4.2 Security
예시
void criticalMethod(String userName) {
// perform security checks
if (!isAlphaNumeric(userName)) {
throw new SecurityException();
}
// do some secondary tasks
initializeDatabase();
// critical task
connection.executeUpdate("UPDATE Customers SET Status = 'Active' " +
" WHERE UserName = '" + userName + "'");
}
- 만약 스트링이 mutable하다면 executeUpdate() 메서드를 실행할 시점에 보안 점검이 안전한지 확실할 수 없다.
- userName에 대한 레퍼런스를 criticalMethod를 호출한 메서드가 가지고 있기 때문에 보안 점검 이후에 userName의 값을 바꿀 수 있기 때문이다
4.3 Synchronization
- immutable하면 thread safe하다고 말할 수 있다.
- 그 이유는 객체의 내부 상태가 생성 후 변하지 않기 때문이다.
- 따라서 immutable한 객체는 멀티 스레드가 동시에 접근해도 문제가 되지 않는다.
4.4 Performance
- 오직 하나의 String객체를 String Pool에 생성하고 여러개의 다른 변수들이 하나의 같은 String 객체를 가르키게하여 메모리 자원을 절약할 수 있다.
5 자주 사용되는 String 메소드
| Modifier and Type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
char | charAt(int index) | Returns the char value at the specified index. |
boolean | equals(Object anObject) | Compares this string to the specified object. |
byte[] | getBytes() | Encodes this String into a sequence of bytes using the platform's default charset, storing the result into a new byte array. |
int | indexOf(String str) | Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the specified substring. |
int | length() | Returns the length of this string. |
String | substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) | Returns a string that is a substring of this string |
String | substring(int beginIndex) | Returns a string that is a substring of this string. |
6 StringTokenizer 클래스
- 문자열이 특정 구분자로 연결되어 있을 경우, 구분자를 기준으로 부분 문자열을 분리 하기 위해서는 String의 split() 메소드를 이용한다.
- 또는 java.util 패키지의 StringTokenizer 클래스를 이용할 수 있다.
- split()은 정규 표현식으로 구분하고, StringTokenizer는 문자로 구분한다는 차이점이 있다.
StringTokenizer 메소드
| Modifier and Type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
int | countTokens() | Calculates the number of times that this tokenizer's nextToken method can be called before it generates an exception. |
boolean | hasMoreElements() | Returns the same value as the hasMoreTokens method. |
boolean | hasMoreTokens() | Tests if there are more tokens available from this tokenizer's string. |
Object | nextElement() | Returns the same value as the nextToken method, except that its declared return value is Object rather than String. |
String | nextToken() | Returns the next token from this string tokenizer. |
String | nextToken(String delim) | Returns the next token in this string tokenizer's string. |
예시
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer("문자열", "구분자");
// 구분자 생략시 공백이 기본 구분자가 된다.
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer("문자열");
// 모든 token 접근 방식1
int countTokens = st.countTokens();
for (int i = 0; i < countTokens; i++) {
String token = st.nextToken();
}
// 모든 token 접근 방식2
while (st.hasMoreTokens()){
String token = st.nextToken();
}
7 StringBuilder 클래스
문자열을 저장하는 String 내부의 문자열을 수정할 수 없다. 예를 들어 String의 replace() 메소드는 내부의 문자를 대치하는 것이 아니라 대치된 새로운 문자열을 리턴한다. 문자열을 더하는 연산도 마찬가지다. 문자열을 결합하는 + 연산자를 많이 사용하면 그만큼 String 객체의 수도 늘어나기에 성능 저하의 요인이된다. 따라서 문자를 변경하는 작업이 많을 경우 String 클래스보다 StringBuffer 클래스 또는 StringBuilder 클래스를 사용하는 것이 좋다.
- 클래스 내부 버퍼에 문자열을 저장해 두고 추가, 수정, 삭제 작업을 할 수 있도록 설계되어 있다.
- StringBuilder와 StringBuffer의 사용법은 동일하다
- StringBuilder는 단일 스레드 환경에서만 사용하도록 설계되어 있다.
StringBuilder는 Thread Safe하지 않다.StringBuffer는 Thread Safe하다
- 버퍼가 부족할 경우 자동으로 버퍼의 크기를 늘리기 때문에 초기 버퍼의 크기는 그다지 중요하지 않다
초기화
// 16개의 문자들을 저장할 수 있는 초기 버퍼를 가진 StringBuilder 생성
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
// 매개변수 capacity 만큼의 버퍼 크기를 가진 StringBuilder 생성
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(16);
// 주어진 문자열 + 16 만큼의 버퍼 크기를 가진 StringBuilder 생성
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Java");
자주 사용되는 메소드
| Modifier and Type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
StringBuilder | append(String str) | Appends the specified string to this character sequence. |
StringBuilder | insert(int offset, String str) | Inserts the string into this character sequence. |
StringBuilder | replace(int start, int end, String str) | Replaces the characters in a substring of this sequence with characters in the specified String. |
StringBuilder | reverse() | Causes this character sequence to be replaced by the reverse of the sequence. |
StringBuilder | delete(int start, int end) | Removes the characters in a substring of this sequence. |
StringBuilder | deleteCharAt(int index) | Removes the char at the specified position in this sequence. |
8 StringBuffer 클래스
문자열을 저장하는 String 내부의 문자열을 수정할 수 없다. 예를 들어 String의 replace() 메소드는 내부의 문자를 대치하는 것이 아니라 대치된 새로운 문자열을 리턴한다. 문자열을 더하는 연산도 마찬가지다. 문자열을 결합하는 + 연산자를 많이 사용하면 그만큼 String 객체의 수도 늘어나기에 성능 저하의 요인이된다. 따라서 문자를 변경하는 작업이 많을 경우 String 클래스보다 StringBuffer 클래스 또는 StringBuilder 클래스를 사용하는 것이 좋다.
- 클래스 내부 버퍼에 문자열을 저장해 두고 추가, 수정, 삭제 작업을 할 수 있도록 설계되어 있다.
StringBuilder와 차이점
- 멀티 스레드 환경에서 사용할 수 있도록 동기화가 적용되어 있어 Thread Safe하다
9 StringBuilder, StringBuffer 비교
- 메서드에 synchronized 키워드를 적용 멀티 스레드 환경에서도 thread-safe하다
StringBuilder의 append 메서드
@Override
@HotSpotIntrinsicCandidate
public StringBuilder append(String str) {
super.append(str);
return this;
}
StringBuffer의 append 메서드
@Override
@HotSpotIntrinsicCandidate
public synchronized StringBuffer append(String str) {
toStringCache = null;
super.append(str);
return this;
}
참고