Fluent-Bit
1 Fluent Bit
- Fluent Bit은 Fluentd의 경량 버전이라고 생각하면 된다.
1.1 Fluent Bit과 Fluentd
Fluent Bit과 Fluentd 비교
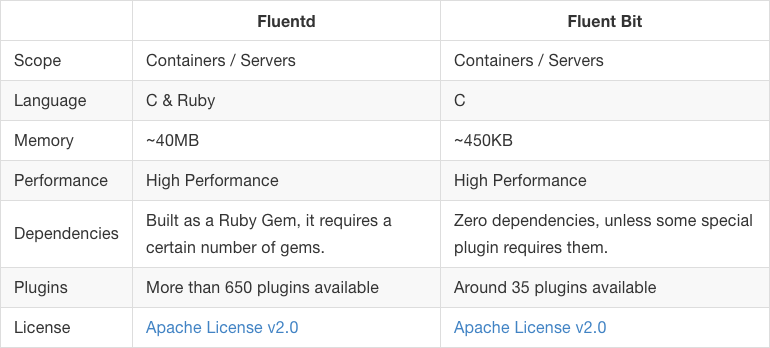
- Fluentd와 Fluentbit은 상호 배타적 관계가 아니다.
- Fluentbit은 Fluentd의 경량 버전이라고 생각하면 쉽다.
- Fluentbit과 Fluentd의 관계는 Beats와 Logstash의 관계와 유사하다.
- https://logz.io/blog/fluentd-vs-fluent-bit/를 참고하자.
Fluent Bit과 Fluentd를 같이 사용하는 아키텍처가 가능하다
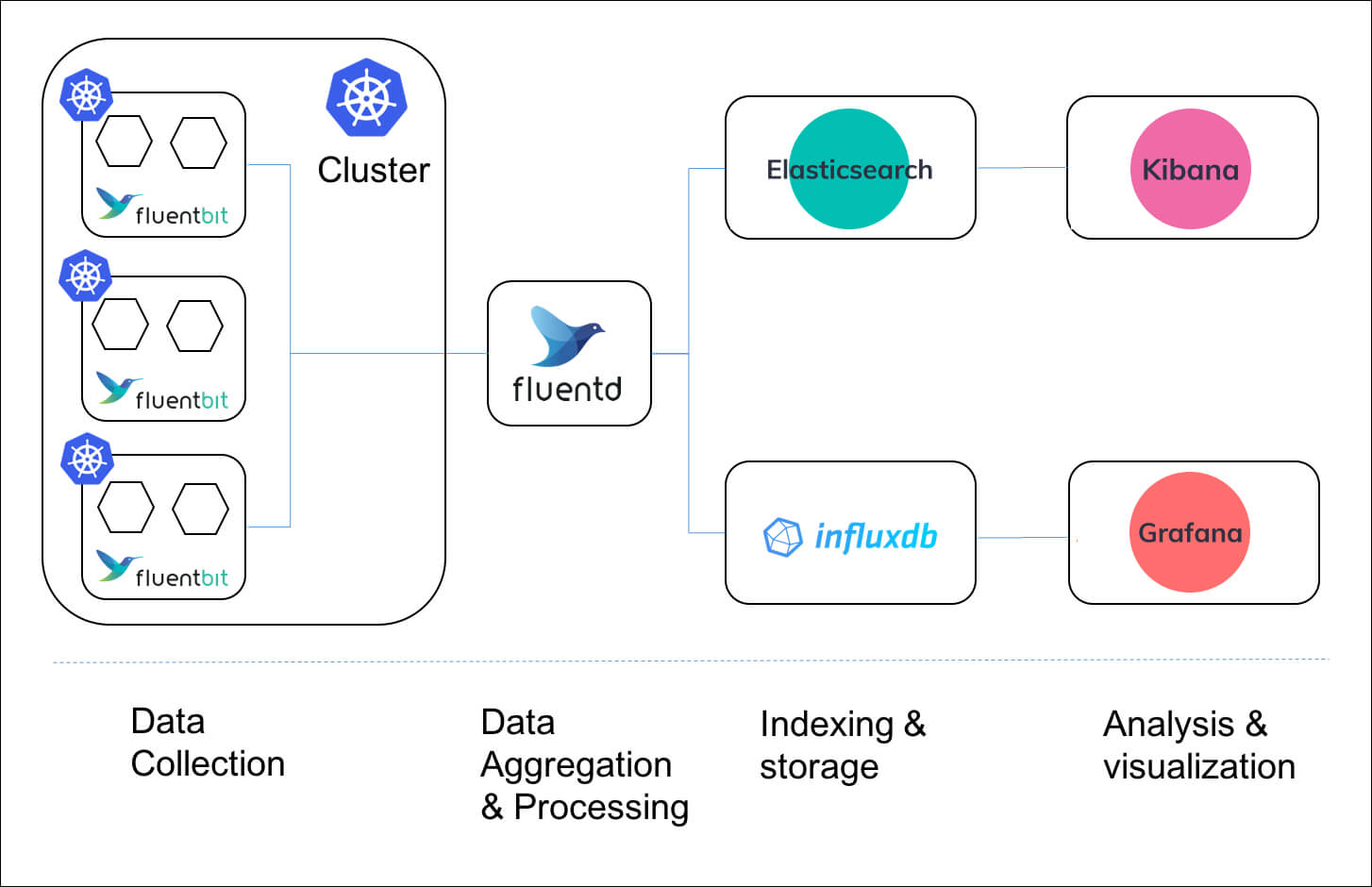
- Fluent Bit을 daemonset을 이용해서 노드마다 하나씩 배포한다.
- Fluent Bit은 데이터를 수집하고 Fluentd로 포워딩한다.
- Fluentd는 클러스터 당 하나의 인스턴스를 배포한다.
- Fluent Bit로부터 받은 데이터를 aggregation하고 다시 포워딩한다.
1.2 Key Concept
1.2.1 Event or Record
- 레퍼런스
- Fluent Bit로 들어오는 모든 데이터 조각들을 Event 또는 Record라고 부른다.
- 데이터: 로그 또는 메트릭
Event의 포맷
- Event는 아래 3가지로 구성된다.
- timestamp
- key/value metadata (since v2.1.0)
- payload
[[TIMESTAMP, METADATA], MESSAGE]
- TIMESTAMP: 초 단위로 표현된 정수 또는 부동소수점 값으로 나타내는 타임스탬프입니다(문자열이 아님).
- METADATA: 이벤트 메타데이터를 포함하는 가능성이 있는 객체
- MESSAGE: 이벤트 본문을 포함하는 객체
Structured Messages
- Messages는 아래와 같이 Structure를 가질수도 있고 아닐수도 있다.
{"project": "Fluent Bit", "created": 1398289291}"Project Fluent Bit created on 1398289291"
- structure가 있는 메시지를 처리하는 것이 더 빠르다.
1.2.2 Tag
- 모든 이벤트에는 Tag가 부여된다.
- Tag는 이후 필터 단계와 아웃풋 단계에서 사용된다.
- 대부분의 Tag는 설정을 통해 직접 부여된다.
- 만약 Tag를 명시하지 않으면 Fluent Bit는 자동으로 인풋 플러그인의 이름을 Tag로 부여한다.
1.3 Data Pipeline
%20(2)%20(2)%20(2)%20(2)%20(2)%20(2)%20(2)%20(1).png?alt=media)
- Fluent Bit로 들어오는 데이터는 아래와 같은 파이프라인을 거친다.
- input
- Parser
- Filter
- Buffer
- Router
- Output
2 Input
- 레퍼런스
- Fluent Bit는 여러 가지 소스로부터 정보를 모으기 위해 여러 Input Plugin을 제공한다.
- 여러 인풋 플러그인 https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/pipeline/inputs 참고
2.1 Tail Plugin
- tail input plugin은 텍스트 파일을 모니터링한다.
tail -f와 유사하게 작동한다.
- Tail은
Path패턴에 매칭되는 모든 파일을 모니터링한다.- 텍스트 파일에 새로운 줄이 추가되면 새로운 이벤트(레코드)를 ��생성한다.
Configuration Parameters
Multiline Support
- Fluent Bit 1.8버전 부터 Multiline 기능이 추가되었다.
- 그래서 현재 old configuration mechanism과 new configuration mechanism 두가지 방식이 존재한다.
- 하위 호환성을 위해 old configuration mechanism은 그대로 남겨두었다.
- new configuration mechanism을 이용하면
multiline.parser라는 키를 이용하면 된다.- multiline.parser를 사용하게 되면 old configuration mechanism인 아래의 키를 사용할 수 없다.
- parser
- parser_firstline
- parser_N
- multiline
- multiline_flush
- docker_mode
3 Parser
- Parser는 structure가 없는 데이터에 structure를 부여하는 역할을 한다.
- 구조가 없는 데이터 처리하는 것은 매우 비효율적이기 때문에 Input 단계에서 구조가 없는 데이터가 들어오면 바로 Parser에 의해 구조를 부여한다.
예시
192.168.2.20 - - [28/Jul/2006:10:27:10 -0300] "GET /cgi-bin/try/ HTTP/1.0" 200 3395
- 위와 같은 구조가 없는 데이터를 Parser를 이용해 아래와 같이 구조를 가진 데이터로 만든다.
{
"host": "192.168.2.20",
"user": "-",
"method": "GET",
"path": "/cgi-bin/try/",
"code": "200",
"size": "3395",
"referer": "",
"agent": ""
}
3.1 JSON Parser
- JSON는 원본 로그 소스가 JSON 형태일 경우 사용할 수 있다.
- 로그 소스를 구조화하고 직접적으로 내부 바이너리 표현으로 변환한다.
[PARSER]
Name docker
Format json
Time_Key time
Time_Format %Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S %z
{"key1": 12345, "key2": "abc", "time": "2006-07-28T13:22:04Z"}
- 원본 로그 소스가 위처럼 JSON 형태일 경우
`[1154103724, {"key1"=>12345, "key2"=>"abc"}]`
- JSON Parser를 거치면 위와 같이 표현으로 변환된다.
3.2 Regular Expression Parser
- 레퍼런스
- Ruby Regular Expression을 사용해서 원본 소스에 구조를 부여할 수 있다.
- Ruby Regular Expression이 제대로 동작하는 아래 사이트에서 테스트할 수 있다.
예시
[PARSER]
Name apache
Format regex
Regex ^(?<host>[^ ]*) [^ ]* (?<user>[^ ]*) \[(?<time>[^\]]*)\] "(?<method>\S+)(?: +(?<path>[^\"]*?)(?: +\S*)?)?" (?<code>[^ ]*) (?<size>[^ ]*)(?: "(?<referer>[^\"]*)" "(?<agent>[^\"]*)")?$
Time_Key time
Time_Format %d/%b/%Y:%H:%M:%S %z
Types code:integer size:integer
위 Parser 설정은 Apache HTTP Server log entry를 정규 표현식으로 구조화한다.
192.168.2.20 - - [29/Jul/2015:10:27:10 -0300] "GET /cgi-bin/try/ HTTP/1.0" 200 3395
위는 Apache HTTP Server log entry로 보시다시피 구조가 없는 상태다.
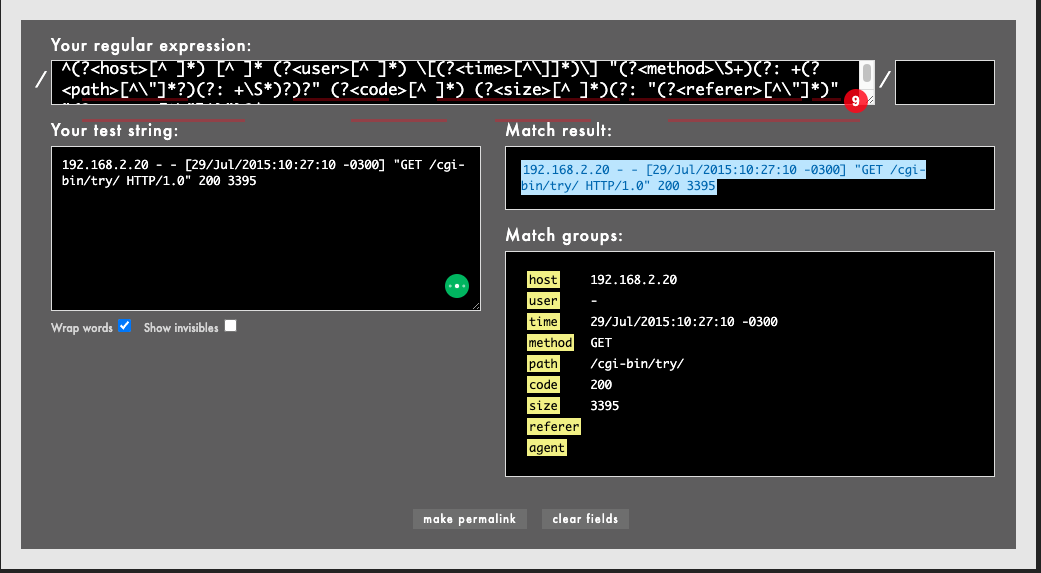
위 정규 표현식 테스트 사이트에 원본 로그 데이터와 정규 표현식을 넣으면 오른쪽 아래와 같이 구조화된 데이터를 얻을 수 있다.
3.1 Parser Plugin
-
기본적으로 Fluent Bit 여러 타입의 로그에 대한 미리 정의된 Parser를 제공한다.
-
Apache
-
Nginx
-
Docker
-
Syslog rfc5424
-
Syslog rfc3164
-
Configuration Parameters
3.3 Multiline Parsing
- 레퍼런스
- 이상적으로, 애플리케이션들은 로그 메시지를 한 줄로 기록할 수 있지만, 실제로는 애플리케이션들이 같은 컨텍스트에 속한 여러 로그 메시지를 생성한다.
- 이런 정보를 처리할 때는 매우 복잡하다.
- 예를 들어, 애플리케이션 stack trace는 항상 여러 로그 라인을 가지고 있기 때문이다.
- Multiline parser를 사용하는 방법에는 2가지가 있다.
- Built-in multiline parser를 이용하기
- Configurable multiline parser를 이용하기
Built-in Multiline Parsers
- 추가 설정 없이 Fluent Bit에서 미리 설정한 Built-in Multiline Parsers를 사용할 수 있다.
- 아래표 참고해서 적합한 Built-in Multiline Parsers가 있다면 바로 사용할 수 있다.
| Parser | Description |
|---|---|
| docker | Process a log entry generated by a Docker container engine. This parser supports the concatenation of log entries split by Docker. |
| cri | Process a log entry generated by CRI-O container engine. Same as the docker parser, it supports concatenation of log entries |
| go | Process log entries generated by a Go based language application and perform concatenation if multiline messages are detected. |
| python | Process log entries generated by a Python based language application and perform concatenation if multiline messages are detected. |
| java | Process log entries generated by a Google Cloud Java language application and perform concatenation if multiline messages are detected. |
Configurable Multiline Parsers
- 레퍼런스
- Built-in Multiline Parsers가 맞지 않는다면 설정을 이용해 커스텀한 Multiline Parsers를 직접 정의할 수 있다.
- Configurable Multiline Parsers는
[MULTILINE_PARSER]키워드를 사용해서 정의한다.
[MULTILINE_PARSER]가 가지는 프로퍼티
| Property | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| name | Specify a unique name for the Multiline Parser definition. A good practice is to prefix the name with the word multiline_ to avoid confusion with normal parser's definitions. | |
| type | Set the multiline mode, for now, we support the type regex. | |
| parser | Name of a pre-defined parser that must be applied to the incoming content before applying the regex rule. If no parser is defined, it's assumed that's a raw text and not a structured message.Note: when a parser is applied to a raw text, then the regex is applied against a specific key of the structured message by using the key_content configuration property (see below). | |
| key_content | For an incoming structured message, specify the key that contains the data that should be processed by the regular expression and possibly concatenated. | |
| flush_timeout | Timeout in milliseconds to flush a non-terminated multiline buffer. Default is set to 5 seconds. | 5s |
| rule | Configure a rule to match a multiline pattern. The rule has a specific format described below. Multiple rules can be defined. |
설정하기
- 파서를 설정하기 전에 알아야 할 것!
- multiline message의 첫 번째 라인과 매칭되는 정규 표현식
- 이어지는 두 번째 라인과 마지막 라인까지 매칭되는 정규 표현식
- 1번 정규 표현식과 매칭되면 start_state 상태라고 한다.
- 2번 정규 표현식과 매칭되면 커스텀한 state 이름을 붙인다.
4 Filter
- 레퍼런스
- Filter가 하는 역할
- 데이터 수정하기
- 데이터에 정보 추가하기
- 데이터 드롭하기
4.1 Kubernetes Plugin
- 레퍼런스
- Kubernetes Filter는 이벤트에 Kubernetes 메타 데이터를 넣어준다.
- Fluent Bit은 쿠버네티스 클러스터에 데몬셋으로 배포했을 때 Fluent Bit이 컨테이너의 로그 파일을 읽고 이벤트를 생성한다.
- 이렇게 생성된 이벤트에 Kubernetes 필터가 아래와 같은 Kubernetes 메타 데이터를 추가해준다.
- Pod Name
- Namespace
- Container Name
- Container ID
- Pod ID
- Labels
- Annotations
5 Buffer
6 Router
- 레퍼런스
- Data 파이프라인을 거친 데이터를 최종적으로 어디로 보낼것인가를 결정하는 역할을 한다.
- 라우팅 과정에서 Tag와 Match가 사용된다.
- Input 단계에서 모든 데이터는 Tag가 부여된다.
- output 단계에서 설정한 Match 룰을 토대로 어디로 보낼지가 결정된다.
예시
[INPUT]
Name cpu
Tag my_cpu
[INPUT]
Name mem
Tag my_mem
[OUTPUT]
Name es
Match my_cpu
[OUTPUT]
Name stdout
Match my_mem
- CPU metrics은 Elasticsearch로 보내고 Memory metrics은 standard output으로 보내는 Match Rule
7 Output
- Input 소스가 다양한 만큼 Output 소스도 다양하다.
- 지원되는 아웃풋 솟 https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/pipeline/outputs 참고